The Structure and Function of Aquatic Microbial Communities: Advances in Understanding

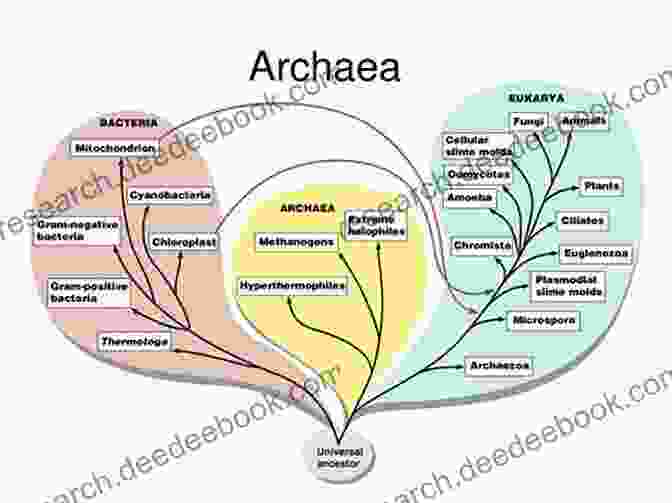
Aquatic microbial communities are complex and dynamic ecosystems that play a crucial role in the functioning of aquatic environments. These communities are composed of a wide variety of microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and protists. Each of these groups has a unique set of physiological and metabolic capabilities, which contributes to the overall functioning of the community.
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 32030 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 633 pages |
The structure and function of aquatic microbial communities are influenced by a variety of factors, including the physical and chemical characteristics of the environment, the availability of resources, and the interactions between different members of the community. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding the structure and function of aquatic microbial communities, as these communities play a vital role in a variety of ecosystem processes, including nutrient cycling, decomposition, and the production of oxygen.
The Structure of Aquatic Microbial Communities
The structure of aquatic microbial communities can be described in terms of the composition, diversity, and abundance of the different groups of microorganisms that make up the community. The composition of a community refers to the types of microorganisms that are present, while the diversity refers to the number of different types of microorganisms that are present. The abundance of a community refers to the number of microorganisms of each type that are present.
The structure of aquatic microbial communities can vary greatly depending on the physical and chemical characteristics of the environment. For example, communities in nutrient-rich environments tend to be more diverse than communities in nutrient-poor environments. Similarly, communities in warm environments tend to be more diverse than communities in cold environments.
The Function of Aquatic Microbial Communities
The function of aquatic microbial communities is determined by the metabolic capabilities of the individual members of the community. These communities play a vital role in a variety of ecosystem processes, including nutrient cycling, decomposition, and the production of oxygen.
Nutrient cycling is the process by which nutrients are transformed from one form to another. Aquatic microbial communities play a key role in nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the environment. These nutrients can then be used by other organisms, such as plants and animals.
Decomposition is the process by which organic matter is broken down into simpler compounds. Aquatic microbial communities play a key role in decomposition by breaking down dead organisms and releasing nutrients back into the environment. These nutrients can then be used by other organisms, such as plants and animals.
The production of oxygen is essential for the survival of aerobic organisms. Aquatic microbial communities play a key role in the production of oxygen by photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen.
Advances in Understanding the Structure and Function of Aquatic Microbial Communities
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding the structure and function of aquatic microbial communities. This interest has been driven by the recognition of the importance of these communities in a variety of ecosystem processes.
A variety of techniques have been developed to study the structure and function of aquatic microbial communities. These techniques include microscopy, molecular biology, and bioinformatics. Microscopy can be used to visualize the different types of microorganisms that are present in a community. Molecular biology can be used to identify the genes that are present in a community and to study the expression of these genes. Bioinformatics can be used to analyze the data that is generated from microscopy and molecular biology studies.
These techniques have provided a wealth of information about the structure and function of aquatic microbial communities. However, there is still much that we do not know about these communities. Future research will focus on understanding the interactions between different members of the community and on identifying the factors that control the structure and function of these communities.
Aquatic microbial communities are complex and dynamic ecosystems that play a crucial role in the functioning of aquatic environments. These communities are composed of a wide variety of microorganisms, each of which has a unique set of physiological and metabolic capabilities. The structure and function of aquatic microbial communities are influenced by a variety of factors, including the physical and chemical characteristics of the environment, the availability of resources, and the interactions between different members of the community.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding the structure and function of aquatic microbial communities. This interest has been driven by the recognition of the importance of these communities in a variety of ecosystem processes. A variety of techniques have been developed to study the structure and function of aquatic microbial communities, and these techniques have provided a wealth of information about these communities. However, there is still much that we do not know about these communities. Future research will focus on understanding the interactions between different members of the community and on identifying the factors that control the structure and function of these communities.
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 32030 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 633 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Library
Library E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Bookmark
Bookmark Glossary
Glossary Preface
Preface Annotation
Annotation Manuscript
Manuscript Classics
Classics Narrative
Narrative Autobiography
Autobiography Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Thesaurus
Thesaurus Resolution
Resolution Librarian
Librarian Catalog
Catalog Borrowing
Borrowing Stacks
Stacks Periodicals
Periodicals Study
Study Research
Research Lending
Lending Reserve
Reserve Academic
Academic Journals
Journals Reading Room
Reading Room Rare Books
Rare Books Interlibrary
Interlibrary Literacy
Literacy Study Group
Study Group Dissertation
Dissertation Awards
Awards Jeremy Cooper
Jeremy Cooper Stephen Brooks
Stephen Brooks Pauline Johnson
Pauline Johnson Matthew Sullivan
Matthew Sullivan Les Robinson
Les Robinson Pascale Vermont
Pascale Vermont Michael Tomz
Michael Tomz Rosanne Brant
Rosanne Brant Bob Orrell
Bob Orrell Jim Krane
Jim Krane Zig Ziglar
Zig Ziglar Dick Davis
Dick Davis Melissa Holbrook Pierson
Melissa Holbrook Pierson Lowell Tarling
Lowell Tarling Izhar Perlman
Izhar Perlman Giuseppe Bonaccorso
Giuseppe Bonaccorso Jeffrey Lant
Jeffrey Lant Anna Giakoumaki
Anna Giakoumaki David Freedberg
David Freedberg Marty Stuart
Marty Stuart
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!
 Dwayne MitchellFollow ·13.5k
Dwayne MitchellFollow ·13.5k Gabriel HayesFollow ·3.1k
Gabriel HayesFollow ·3.1k Bernard PowellFollow ·9.6k
Bernard PowellFollow ·9.6k Clark CampbellFollow ·12.9k
Clark CampbellFollow ·12.9k Eli BlairFollow ·4.3k
Eli BlairFollow ·4.3k Elliott CarterFollow ·7.3k
Elliott CarterFollow ·7.3k Rob FosterFollow ·6.9k
Rob FosterFollow ·6.9k Steve CarterFollow ·4.8k
Steve CarterFollow ·4.8k

 Corbin Powell
Corbin PowellMy Little Bible Promises Thomas Nelson
In a world filled with uncertainty and...

 Tyler Nelson
Tyler NelsonPolicing Rogue States: Open Media Series Explores Global...
In today's interconnected...

 Bret Mitchell
Bret MitchellMusical Performance: A Comprehensive Guide to...
Immerse yourself in the...

 Juan Rulfo
Juan RulfoLong Distance Motorcycling: The Endless Road and Its...
For many, the...

 Blake Kennedy
Blake KennedyVocal Repertoire for the Twenty-First Century: A...
The vocal repertoire of the twenty-first...

 Eric Hayes
Eric HayesOne Hundred and Ninth on the Call Sheet! The Enigmatic...
In the vast panorama of Western films,...
4.2 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 32030 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 633 pages |